Combining different types of data based on where they are on a map can tell us a lot. Spatial Join, a useful tool in Geographic Information Systems (GIS), helps us do just that. Spatial Join with intersect clause, in this article, Let’s explore how it works and why it’s important.
Key Concept to spatial join with intersect clause
Spatial Join is like putting puzzle pieces together on a map. It helps us merge different sets of data by looking at where things are located. Alongside this guide, datasets will be provided for practical application. Additionally, articles like “Creating Travel Guides: Mapping with GIS Buffer Zones” and “Creating GIS Solutions for Urban Agriculture Map” offer deeper insights into GIS applications.
MAPOG Map Analysis, a simple tool designed to simplify the creation and interpretation of travel maps.
Embarking on a Spatial Join in GIS involves a structured method, enabling analysts to seamlessly merge geographic data and enrich spatial analysis. Let’s explore the step-by-step process:
Step1: Identify Datasets:
First, we pick the data we want to merge. With MAPOG Map, we can easily add map data by clicking a button and choosing the data we need, like country borders and city locations.
1. Click on the “Add Upload” button and choose “Add GIS Data”.
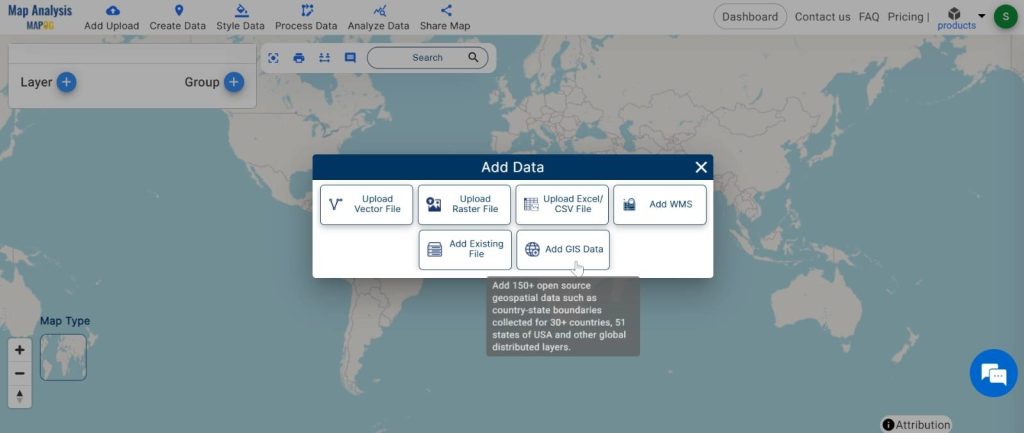
2. Here search the country name.
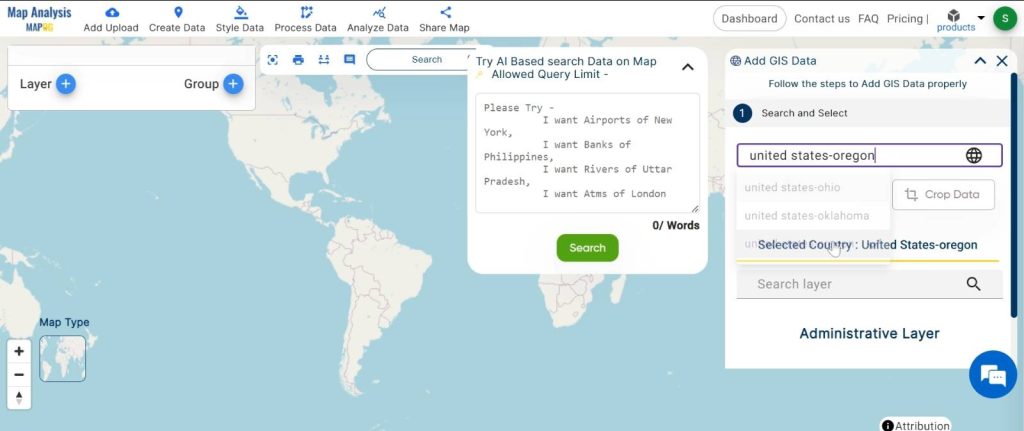
3. Now add the data.
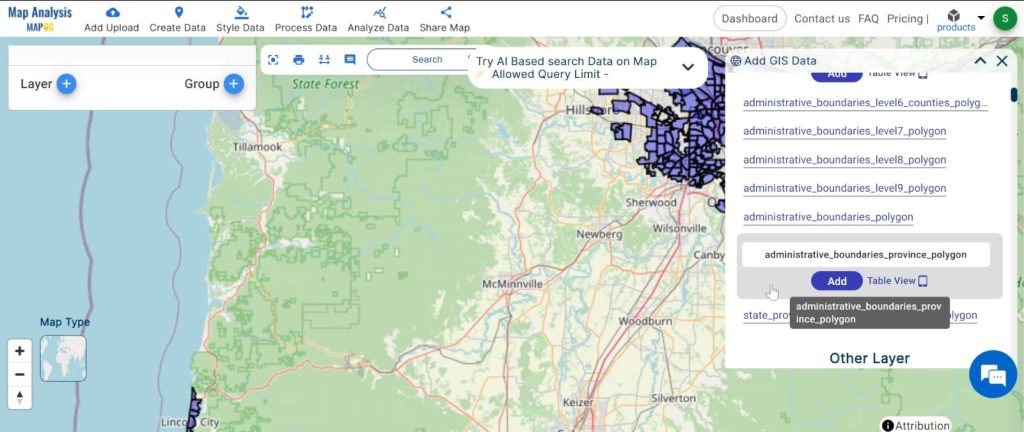
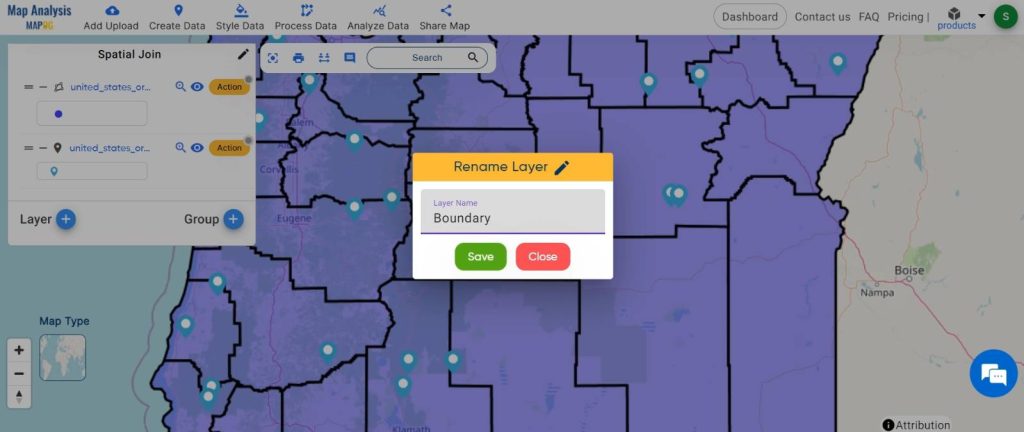
Step2: Name the untitled map and Rename the layer:
1.Here you have to name the untitled map
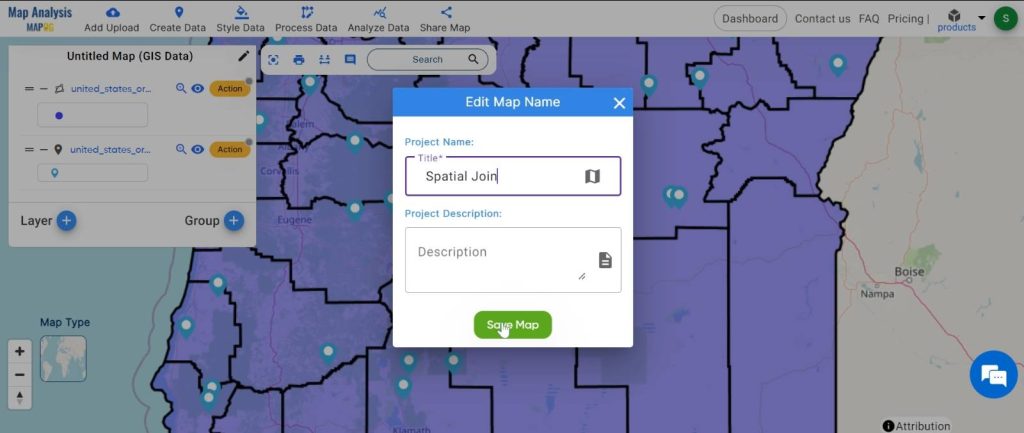
2.Rename the layer
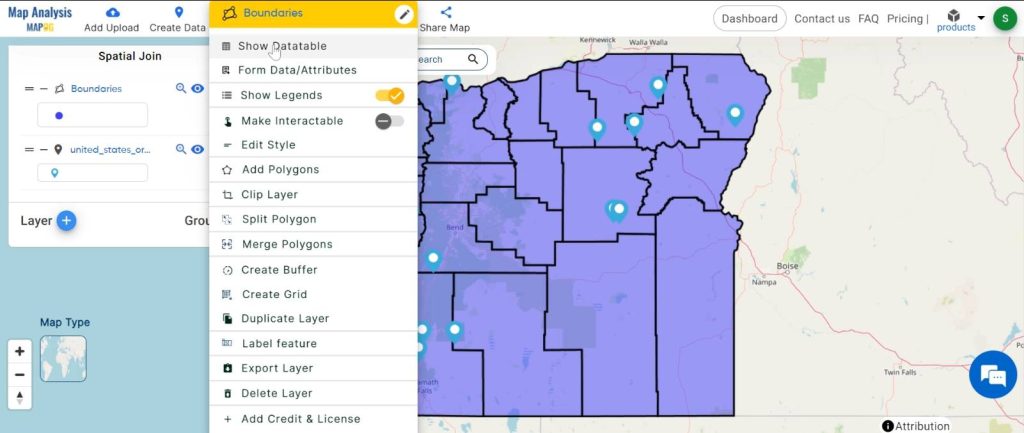
Step3: Define Spatial Relationship:
Next, we decide how the data should fit together on the map. We might want to see where things overlap, where one thing contains another, or where one thing is inside another.
1. Click on the action Button then choose the “Show DataTable” option.
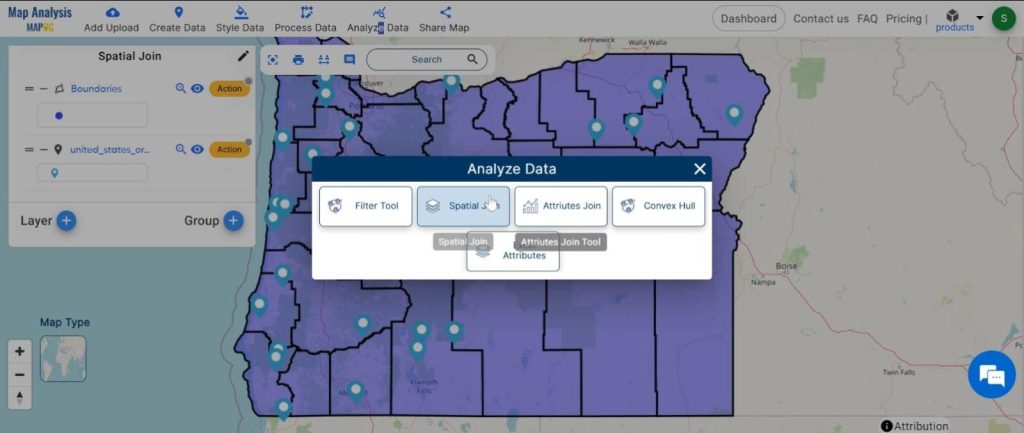
Step4: Execute Spatial Join Operation:
Once we’ve decided how the data should fit, we put it all together. We tell the computer to merge the data based on our instructions. Then, we let the computer do its work.
1.Click on the “Analyze Data” option and choose “Spatial join”.
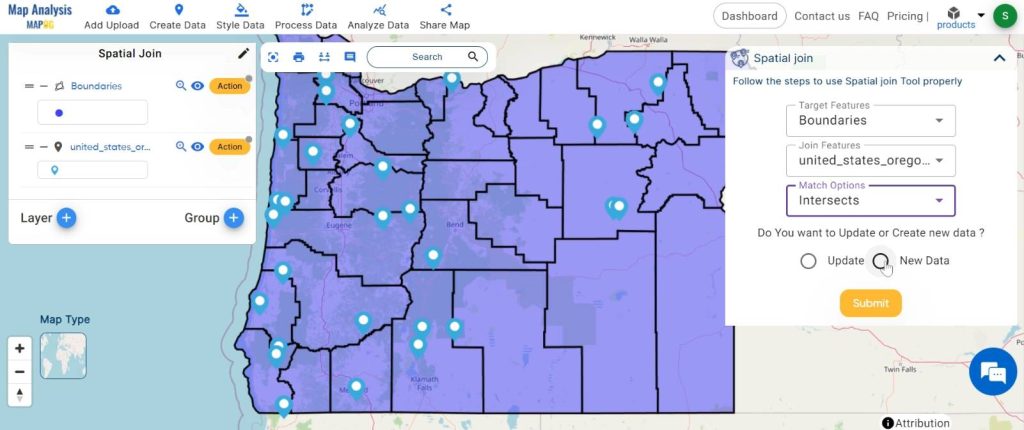
2.Here set the targeted feature and joined feature and the Match option “Intersects”.
Now We can update our data or create a new data layer. Let’s set the join operation and click on the “Submit” button.
Step5: Share Results:
Finally, we share the map we’ve created with others. This helps us all understand the data better and make smarter decisions.
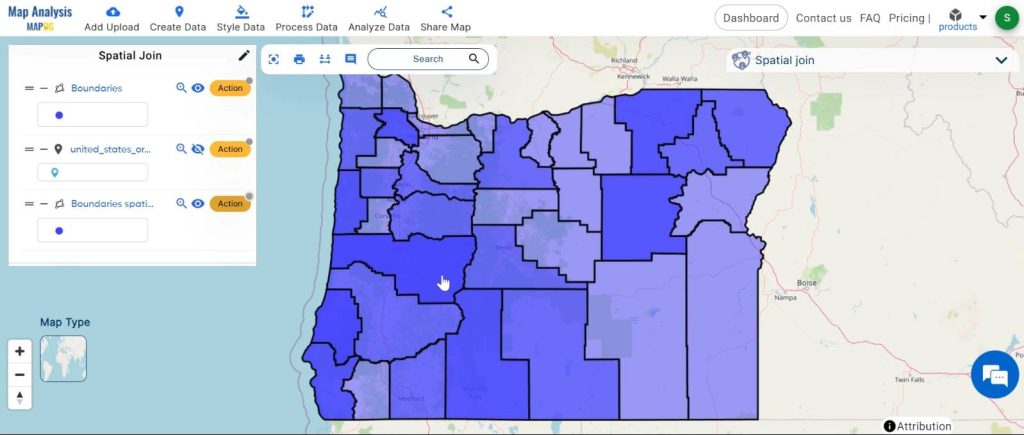
Major Findings:
Using Spatial Join, we can discover new things by looking at the data in a different way. For example, by combining data about farming with maps of different regions, we can learn about where crops are grown and how much land is used.
Domain and Industry Applications:
Spatial Join is useful in many areas. In farming, it helps farmers plan where to grow crops more efficiently. In city planning, it helps decide where to build roads and houses. It’s also important in studying the environment, transportation, health, and responding to disasters.
Spatial Join with MAPOG Map Analysis is a powerful tool for understanding data on maps. By combining different sets of data, we can see connections and patterns that help us make better decisions. It’s a simple but effective way to unlock valuable insights from geographic data.
Link of the Data:
Explore the data further through our GIS Data product, uncovering valuable information for in-depth analysis and understanding.