Spatial Join is a powerful geographic operation in GIS (Geographic Information Systems) used to combine data from two or more layers based on their spatial relationships. A key aspect of Spatial Join is the ‘within’ clause, which specifies that we want to join features based on whether they fall within a specified boundary.
GIS allows us to analyze spatial data to gain insights into various geographic relationships. One common application is to determine how different features interact within specific boundaries. In this guide, we’ll use the example of detecting green spaces within urban environments to illustrate how to perform a “Spatial Join With ‘Within’ Clause” using MAPOG, a powerful GIS tool.
Key Concept:
The ‘within’ clause in Spatial Join specifies that we want to join features that fall within the boundaries of another feature. This is useful for various analyses, such as finding green spaces within city limits, schools within districts, or lakes within parks. Check out our other blog Joining Data To GeoJSON File.
Process For Spatial Join With Within Clause:
Step 1:
Open MAPOG Map Analysis Interface:
Begin by opening the MAPOG map analysis interface, which provides a user-friendly environment for managing and analyzing spatial data.
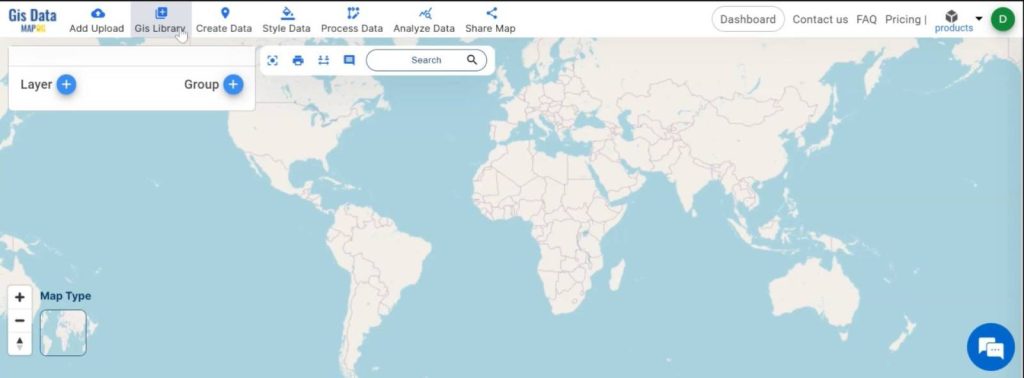
Step 2.
Add Data Layers:
- Go to the GIS library and search for data by country.
- Then, choose your preferred data, such as an administrative boundary layer for the city.
- Follow the same process to add another layer, like green spaces (Greenfield polygon data).
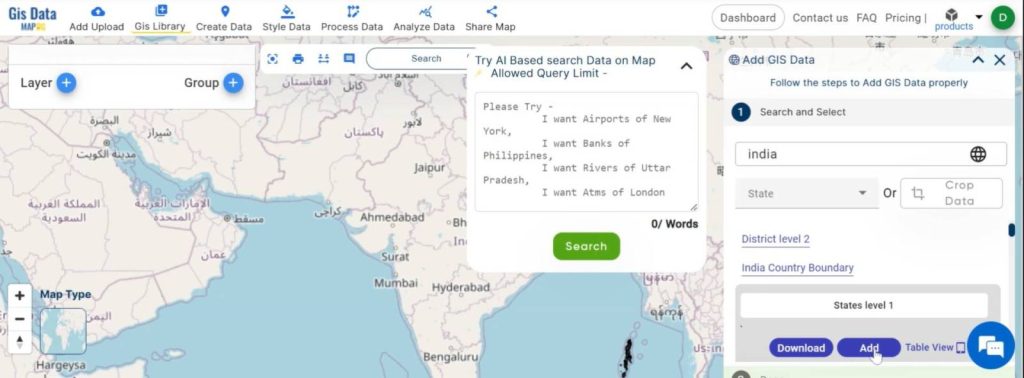
Step 3.
Save the Map:
After adding the layers, name your map using the edit map name option, then click ‘save map’ to ensure your project is saved.
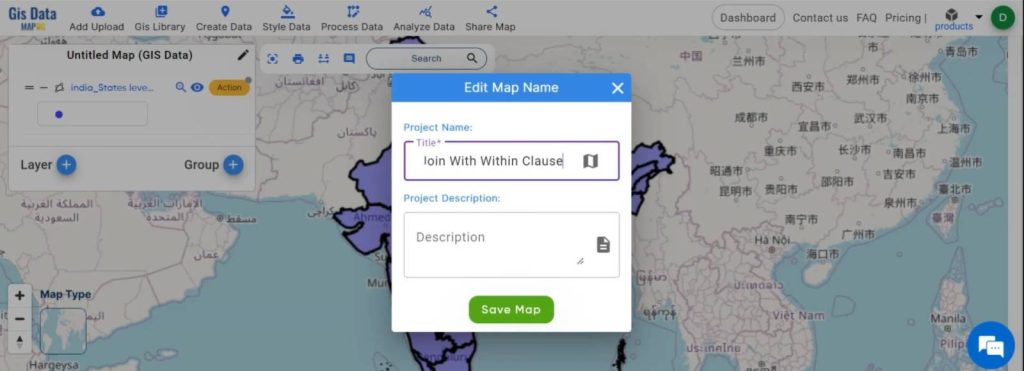
Step 4:
View Data Tables:
Use the show data table option to view the databases of both layers, allowing you to verify the data before performing the spatial join.
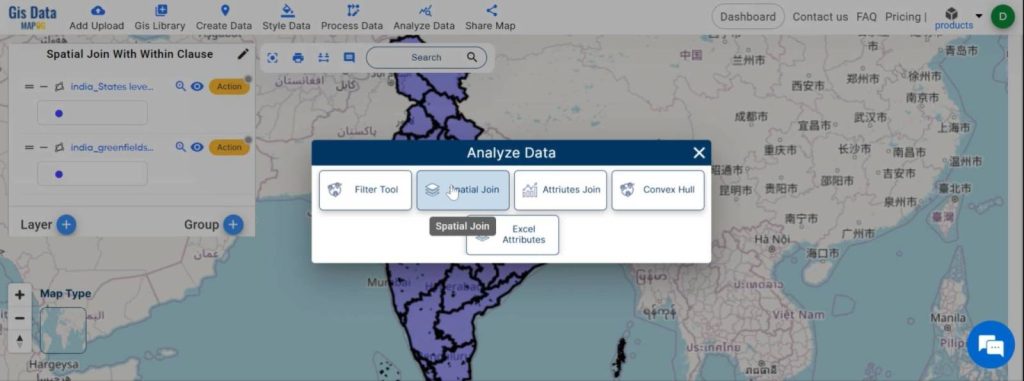
Step 5:
Perform the Spatial Join:
- Go to the ‘Analyze data‘ section, then choose the ‘spatial join‘ option.
- Then, select the target features (e.g., urban boundaries) and join features (e.g., green spaces).
- After that, choose the match option ‘within’ to ensure that green spaces within the urban boundaries are selected.
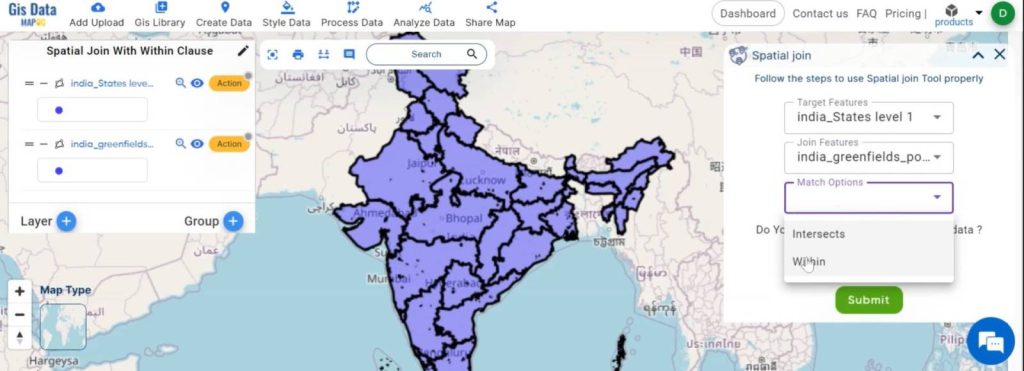
Step 6:
Configure Spatial Join Settings:
- Click on new data and ensure the keep all targeted features option is enabled.
- Then, select the joining operation as one-to-one.
- After that, choose the fields and merge options as required.
- Submit the join operation.
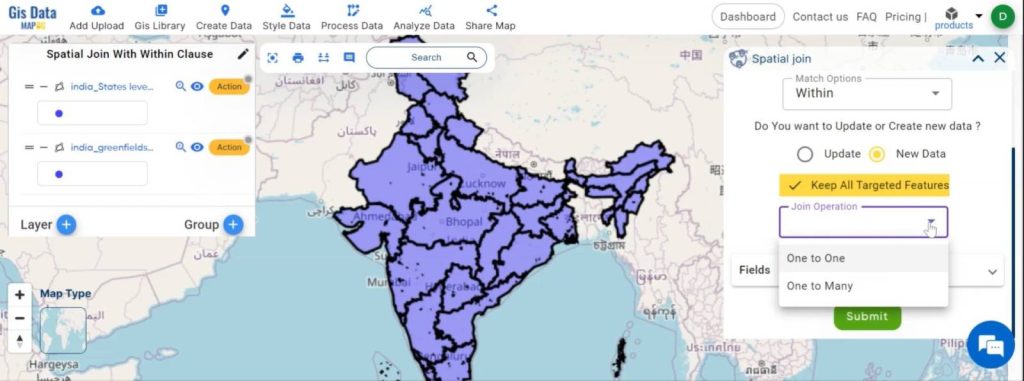
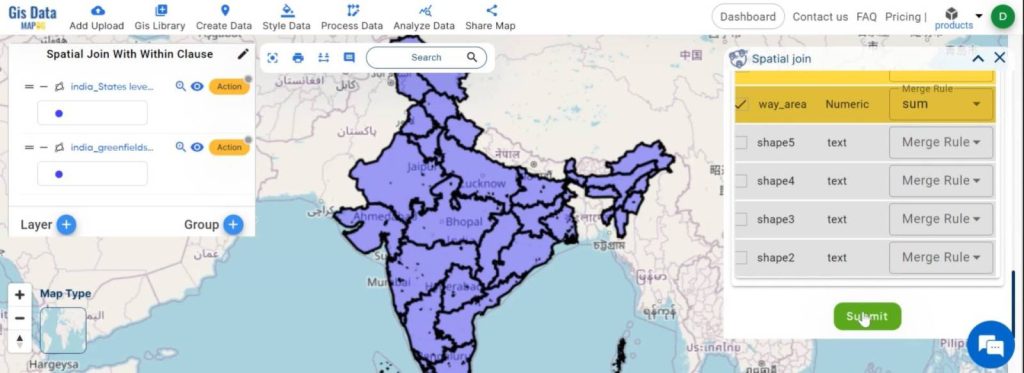
Step 7:
Review Joined Data:
A new layer is created now. Click on the action button and select Show data table to review the combined dataset.
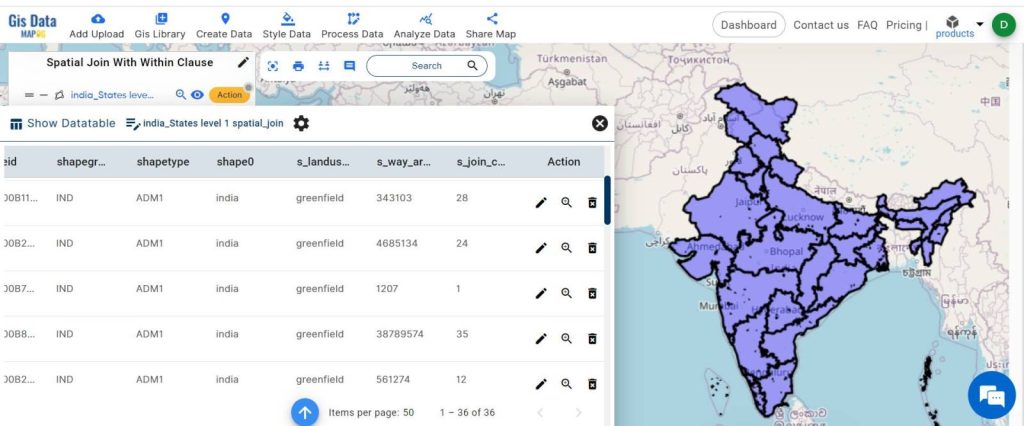
Industry and Domain:
- Identification of Green Spaces: Easily identify areas with abundant green spaces within urban boundaries. This helps in understanding the current distribution and accessibility of green areas for city residents.
- Urban Planning: The analysis can highlight regions lacking sufficient green spaces, informing urban planners where new parks or green infrastructure might be needed.
- Resource Allocation: Data-driven decisions can be made about where to allocate resources for the maintenance and development of green spaces, ensuring equitable access across the city.
Conclusion:
Spatial join with the ‘within’ clause is a valuable tool for analyzing spatial relationships in GIS. It allows us to see how features interact within specific boundaries. Providing insights that can inform urban planning and other geographic analyses. By mastering this technique, users can leverage GIS tools like MAPOG to create detailed, informative maps and make better decisions based on spatial data.
Link of The Data:
Previous Blog Links:
Grid Mapping for Accurate Spatial Analysis: Divide and Conquer with GRID Map Tool
Create a Map: Spatial Join Analysis of ATM Points within District Boundaries