In today’s global landscape, the management and distribution of agricultural land have become critical factors in ensuring sustainable food production and equitable resource access. However, many regions face challenges with fragmented land ownership patterns and inefficient land use practices, hindering optimal agricultural productivity and creating socioeconomic disparities. In this context, mapping the farmlands with equitable agricultural land has become relevant. MAPOG addresses these challenges with Agricultural Land Consolidation and Redistribution using merge and split tools and thus revolutionizing agricultural land management for the betterment of communities and ecosystems alike.
Key Concept- Mapping for Agricultural Land Redistribution
By leveraging GIS data, MAPOG facilitates the identification of suitable areas for consolidation and redistribution of agricultural lands. And integrates those geographical data with various analytical tools to support decision-making in land management. The split and merge tools within the MAPOG platform enable the reorganization of land parcels by merging the adjacent fragmented lands into a single unit and then dividing the parcel into equal parts. The links for GIS Data which we’re using here are mentioned at the end of the article.
Follow the below process Step-by-Step for agricultural land redistribution:
Step 1: Open Map Analysis
Open Map analysis interface from MAPOG platform
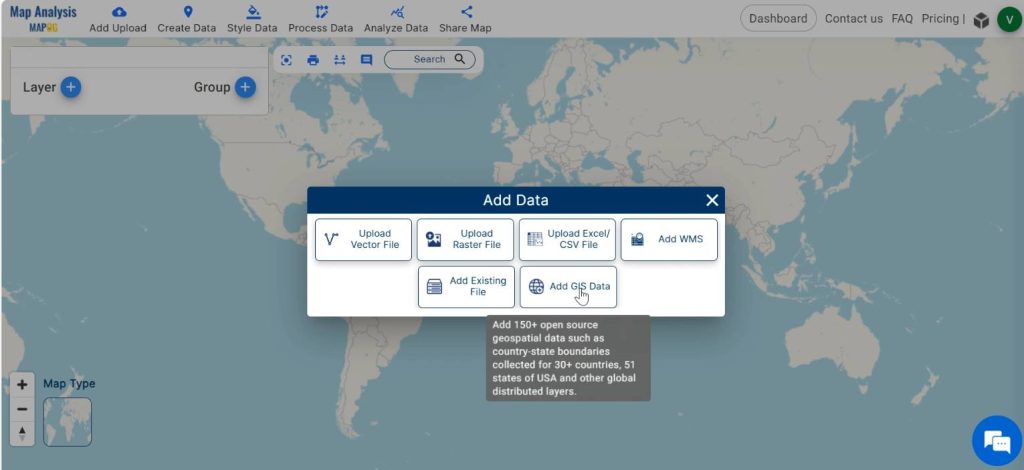
Step 2: Upload Data
, Click on Add upload in the header. Select Add GIS data.
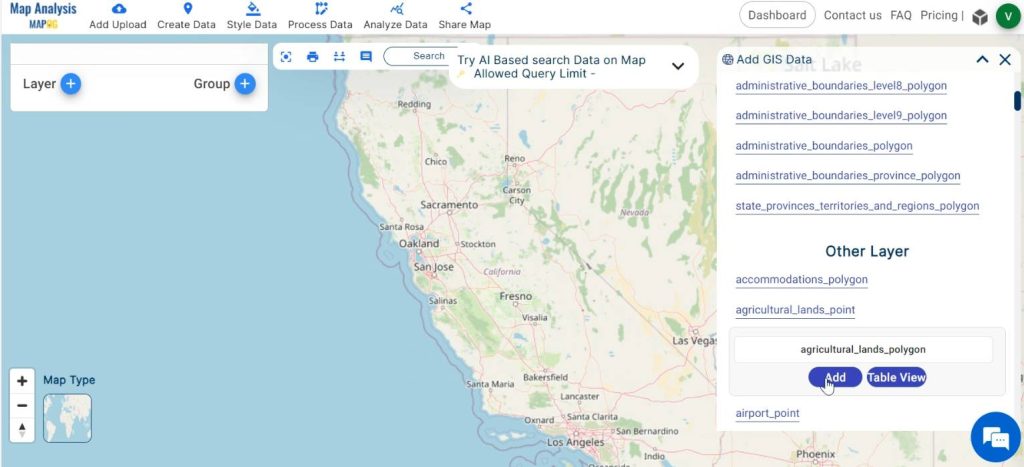
Then, select the country and add agriculture land polygons from the built-in GIS data.
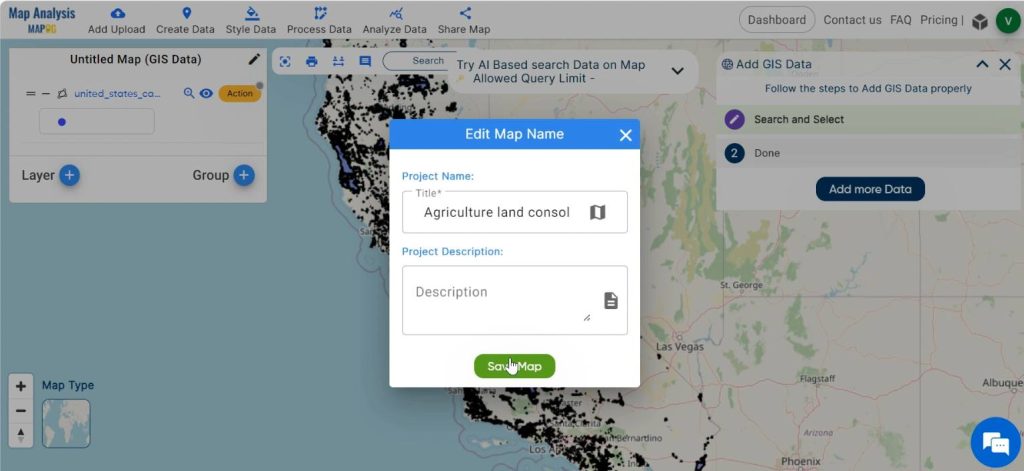
Step 3: Save your Map
Now, save your map with suitable names by clicking on the pencil icon seen near the “Untitled Map” text.
Step 4: Clip the layer
For your convenience, extract out the specific agricultural land of your interest by using the Clip tool. Click on Action then select Clip layer option. By enabling the icons appearing in the dialogue box, draw a polygon around your region of interest. Then click on Submit.
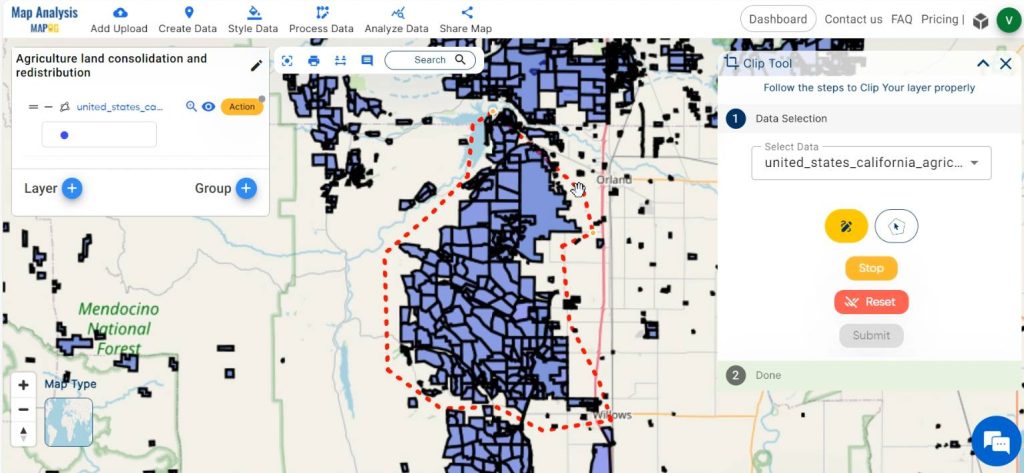
Hide the agriculture land polygon layer initially added.
After that, rename the clipped layer by clicking on the pencil icon in the Action.
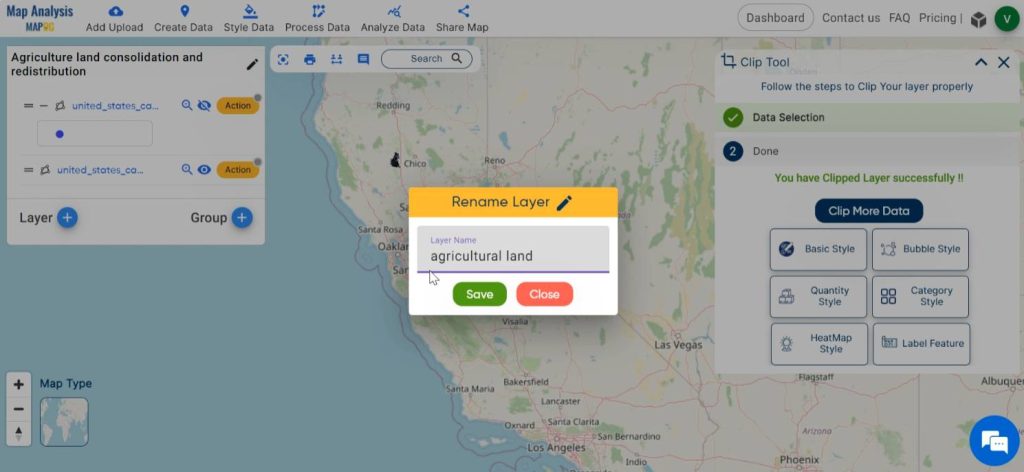
Step 5: Consolidate the agricultural land
Next, click on Process data and select Merge polygons.
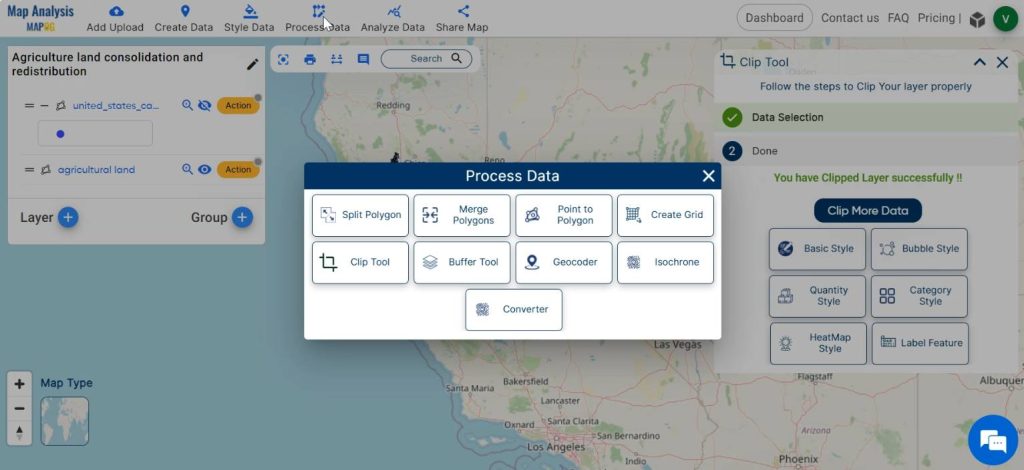
Select the polygon to be merged either by drawing a polygon intersecting the desired polygon using Lasso tool or select it manually by left clicking on the polygon. Then click on New Layer to publish the merged data.
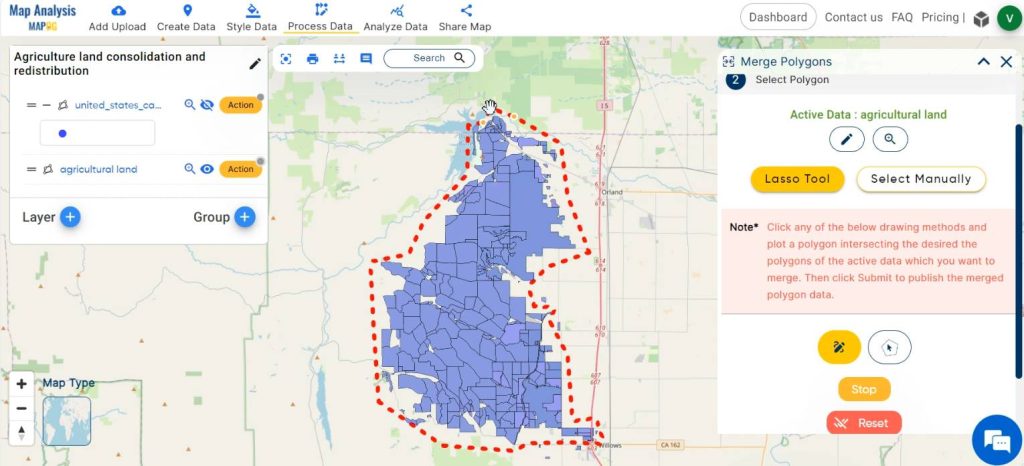
Hide the clipped layer to see the merged polygon.
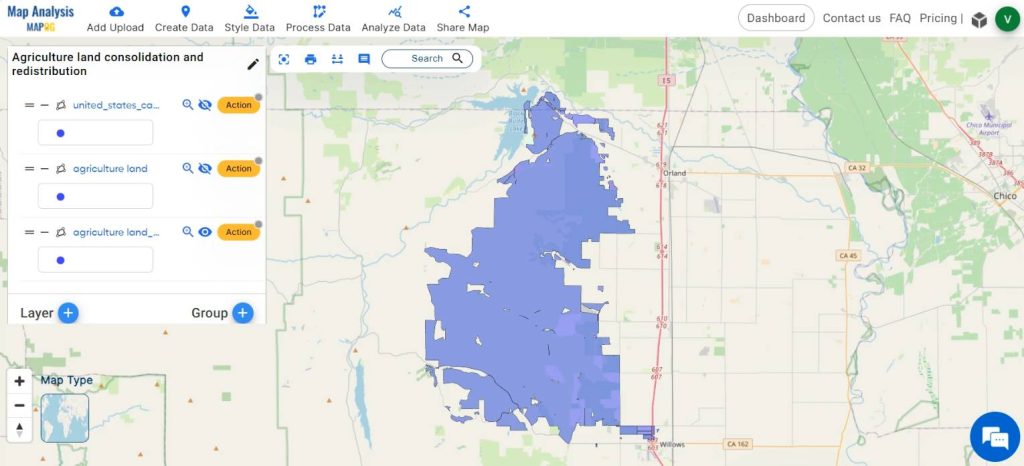
Step 6: Redistribute agricultural land
For redistributing, click on Process data and select Split polygon.
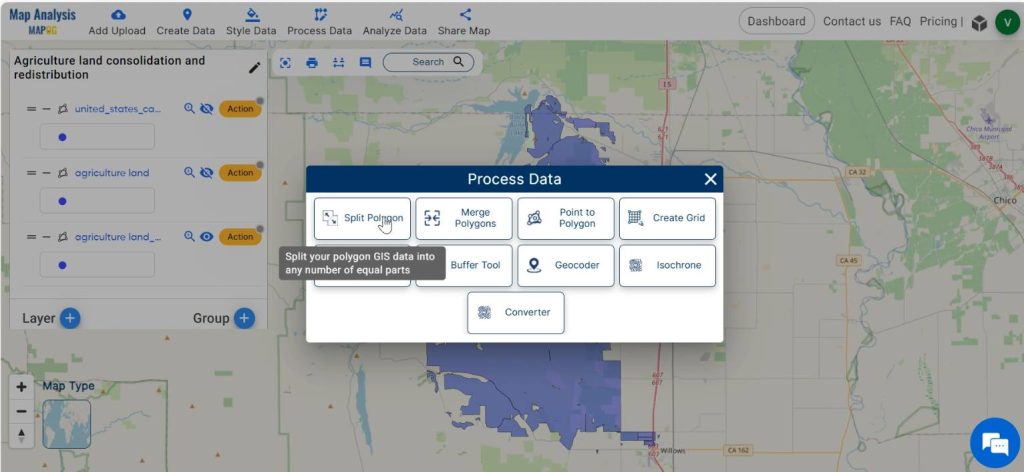
Then select the layer and select the polygon in the active data by left clicking on the polygon. Enter the number of parts to which the polygon has to be splitted equally. Finally click on the New layer.
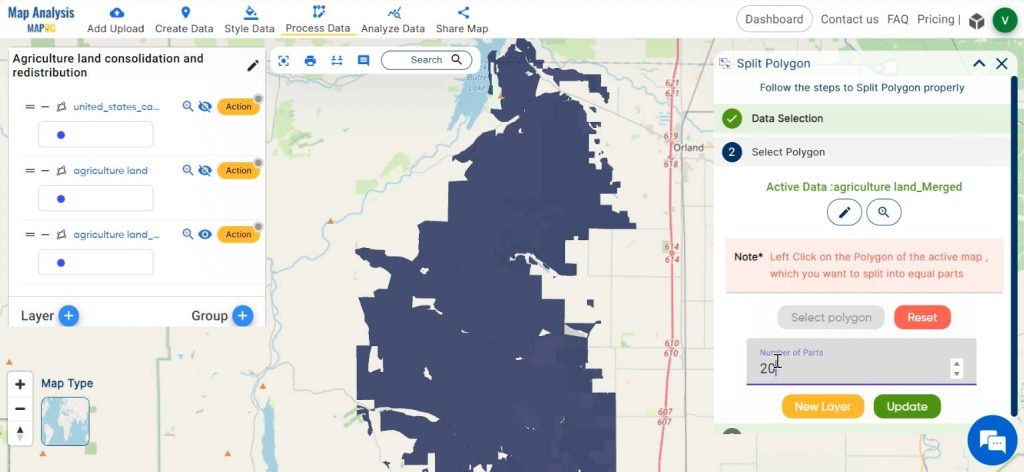
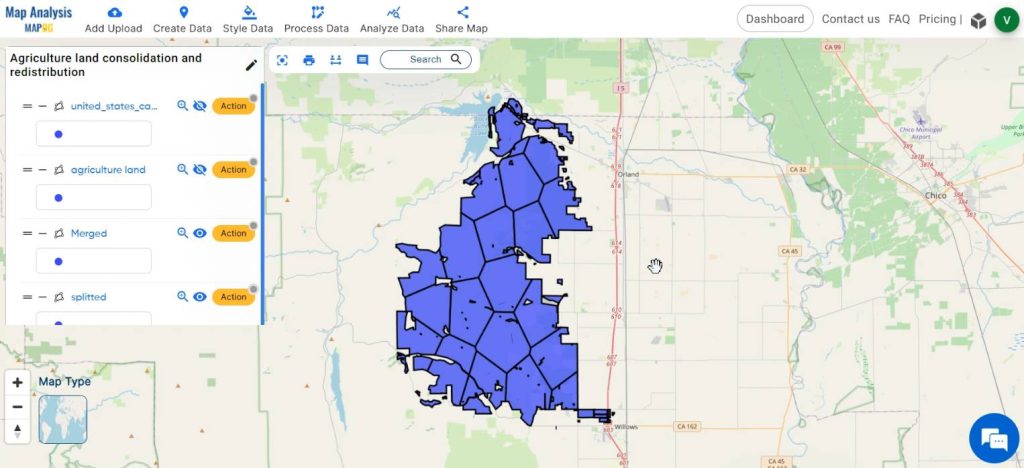
Now the polygon is splitted equally i.e, the agricultural land is redistributed equally.
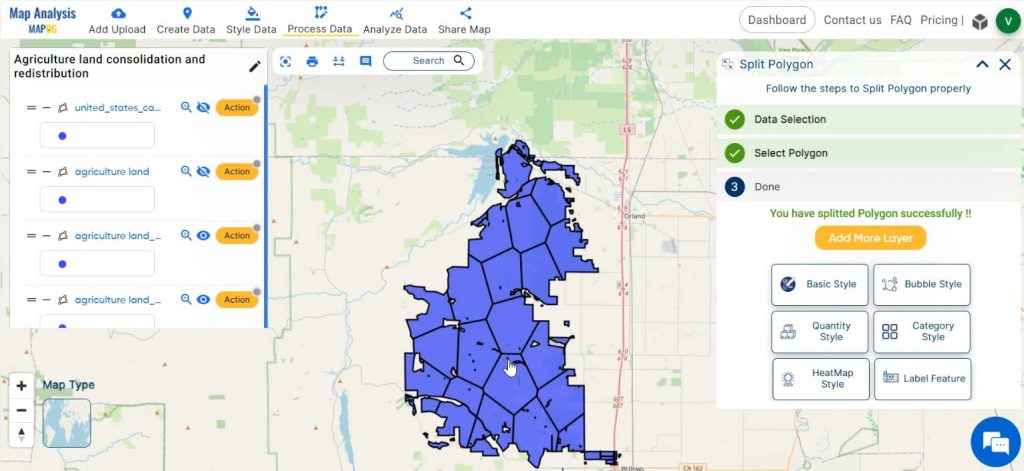
Step 7: Final adjustments
Rename the layers with appropriate names and do any other final adjustments, if required.
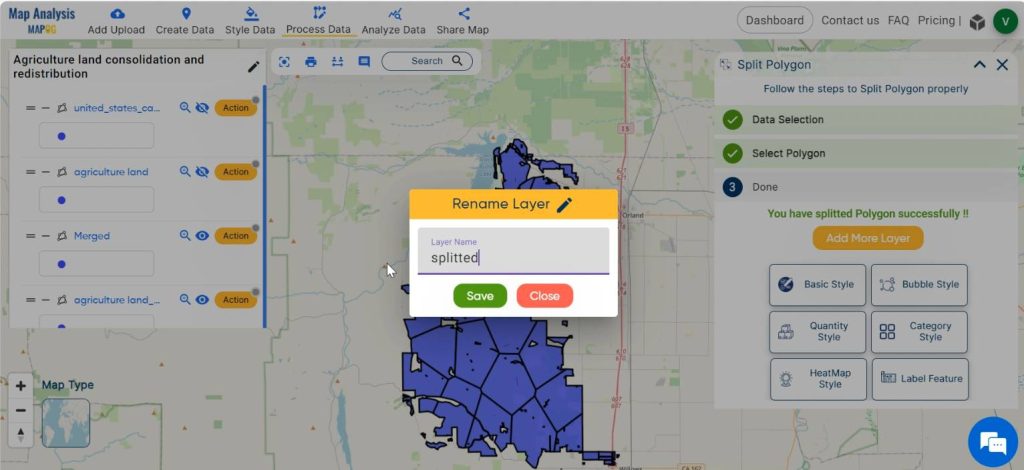
Finally we have created a map which shows the redistribution of agricultural land into equal parts.
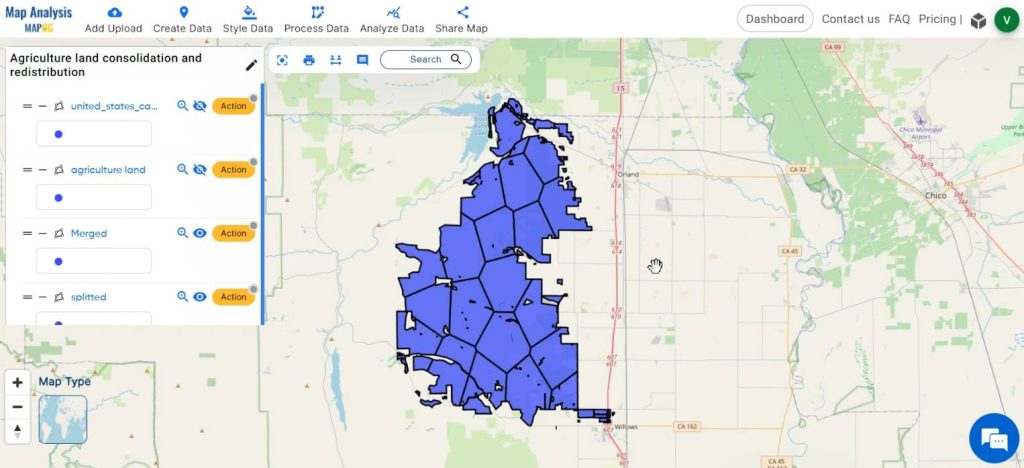
Step 8: Share the map
And now you can share the map using the Share tool.
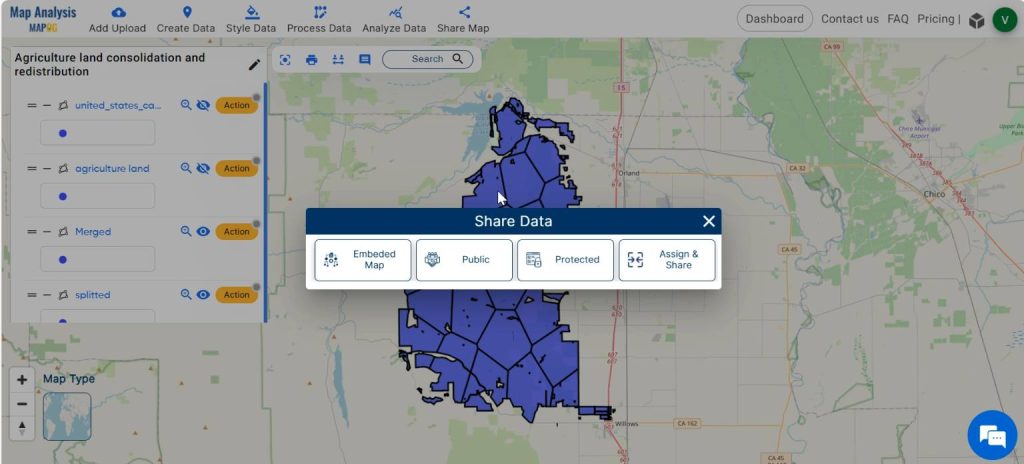
Major Findings- Mapping for Agricultural land redistribution
The major findings and insights of Agriculture Land Consolidation and Redistribution using merge and split tools in MAPOG include:
1. Parcel Optimization: The merge tool helps to consolidate fragmented land parcels into larger, contiguous units leading to more efficient land use patterns, reducing fragmentation-related inefficiencies, and improving accessibility for agricultural activities.
2. Land Suitability Analysis: Land redistribution results in parcels that are better suited for agricultural production.
3. Equity and Social Impacts: The redistribution of land aims to promote equity in land access and ownership, particularly among smallholder farmers and marginalised communities
4. Economic Viability: It can help evaluate the economic viability of land consolidation and redistribution by estimating potential productivity gains, cost savings, and revenue generation opportunities resulting from more efficient land use.
5. Environmental Considerations: Land consolidation and redistribution have effects on biodiversity, soil conservation, and water management. This enables the integration of environmental data to assess the ecological impacts of land redistribution initiatives and identify strategies to minimize negative consequences while maximizing sustainability.
6. Policy and Governance: Findings regarding land tenure, governance structures, legal frameworks, and institutional capacities can inform the design and implementation of policies and programs aimed at promoting equitable and sustainable land management practices.
In overall, land redistribution with merge and split tools in MAPOG contribute to a better understanding of how land consolidation and redistribution can address land fragmentation, enhance agricultural productivity, promote socio-economic development, and achieve broader sustainability goals in rural areas.
Domain and Industry- Mapping for Agricultural land redistribution
The beneficiaries of agricultural land consolidation and redistribution include:
1. Farmers: Smallholder farmers, landless agricultural workers, and other individuals involved in agriculture receive more equitable access to land resources through redistribution initiatives.
2. Local Communities: Communities residing in rural areas where land consolidation and redistribution take place may benefit from increased agricultural productivity, improved livelihoods, and enhanced social cohesion.
3. Government: Governments and regulatory authorities benefit from improved land use efficiency, increased agricultural productivity, and socioeconomic development in rural areas, which can lead to broader economic growth and stability.
4. Environment: Environmental benefits also occur from land consolidation and redistribution initiatives, such as reduced soil erosion, improved water quality, and enhanced biodiversity conservation through more sustainable land management practices.
5. Investors: Private investors and businesses involved in agriculture may benefit from more efficient land utilization and increased agricultural productivity resulting from land consolidation and redistribution efforts.
Conclusion– Mapping for Agricultural land redistribution
In brief, land consolidation and redistribution using MAPOG, offer a holistic approach to addressing land fragmentation and enhancing agricultural productivity. By leveraging MAPOG tools, governments, policymakers, and agricultural stakeholders can optimize land use, promote sustainable development, and improve livelihoods in rural communities. As the global population grows and agricultural landscapes evolve, the integration of MAPOG into land management strategies can become indispensable for ensuring food security, economic growth, and environmental sustainability.
Link to Data
Other Articles
- Protecting Wetlands: Guide to Create GIS Map for Nature
- GIS Analysis in Urban Planning: Reshaping Transportation Future Insights of state/city
- Fast Emergency Response: Using GIS and Isochrone Maps for 10-Minute Ambulance Arrival
- Mapping Tiger Attack Hotspots – Create an Online Map and Share
- Make Routes for Military Aerial Planning- Through Bearing angle and Distance calculation – Online Route Compass
- Mapping Healthcare Efficiency: GIS Buffer Analysis of Hospital Locations
- Add WMS- Two step online view of WMS layer on a map
- Plot ATM locations on a map and embed on your website
- Map habitat locations of endangered animals & keep track of their living