In the realm of geospatial analysis, this article “Creating Maps: Unraveling River-Dam Relationships via Geospatial Analysis,” delves into unraveling the intricate relationships between natural features and human infrastructure. The focus is on employing MAPOG to analyze river networks and their connections to dams, transcending the conventional boundaries of geographical confines. Join us in this exploration where the application of MAPOG becomes instrumental in unlocking the complexities of landscape dynamics, providing a profound understanding of spatial relationships.
Key Concept to Creating Maps: Unraveling River-Dam Relationships
Through the use of MAPOG, employing techniques like category styling and proximity analysis, the study aims to unveil valuable insights into spatial patterns. The implications of these findings extend across diverse domains, including hydroelectric power generation, agriculture, and urban planning. The process involves creating maps as visual representations, contributing to a profound understanding of the intricate relationships within river networks and dams. For readers interested in accessing the data utilized in this study, the link will be provided at the end of the article.
Below, we present the step-by-step process to actualize our mapping exploration using the user-friendly MAPOG Map Analysis tool.
Think of it as your guide, effortlessly revealing the nuances of land cover classifications and protected area boundaries. Let’s embark on this uncomplicated journey, breaking down the process that transforms this GIS endeavor into an accessible and enlightening adventure.
Step1: Upload your River and Dam Data:
Open MAPOG and seamlessly import your primary datasets: the river line vector data and the water body point data containing dam locations. It’s crucial to ensure that your datasets are well-prepared and correctly georeferenced, setting the foundation for accurate and meaningful spatial analysis.
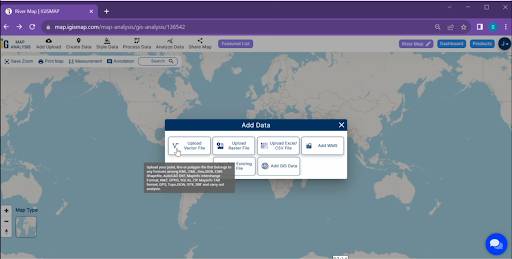
- Click on the “Add Data” button and Choose “Upload Vector File” option.
- You can see the “Upload Vector File” Tool successfully open on the right side of your screen. Here You have to select your Bus Stop data. Click on the “Browse” button.
- click on the “Upload” button.
Step2: Apply Category Styling:
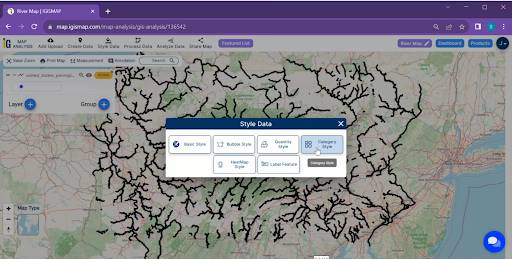
With your datasets securely loaded, navigate to the styling options within MAPOG. Here, you’ll find the ‘Category Style‘ feature, a powerful tool for visual categorization. Opt for ‘Name’ as the attribute for categorization, allowing each river segment to be color-coded based on its name.
- Click on the “Style Data” button and choose the “Category Style” option.
- Here you have to select the agriculture layer and click on the “category circle” option. change the line colour now select the attribute “Name” and click on the save style button.
Step3: Perform Proximity Analysis:
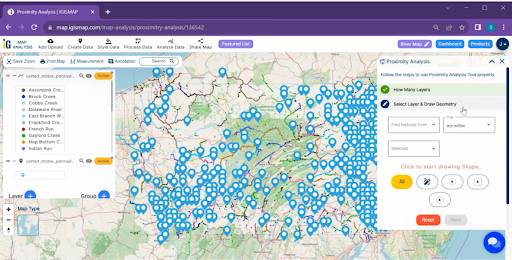
The real magic happens with proximity analysis, a cornerstone of spatial exploration. Head to the ‘Proximity Analysis’ tool in MAPOG, designating your river dataset as the source and the dam dataset as the target. Fine-tune the analysis parameters to fit your specific needs, specifying distance thresholds and other relevant options.
The utilisation of the ‘Proximity Analysis‘ tool.
- Click on the Analyze Data Button and Click on the “Two Layer” Option.
- select the finding features are within and select features. Click on the “next”.
- Write the field name and click on the “get result” option. we have the total Feature
- we can download the excel file and click on the “Publish” Button for visualisation.
Step4: Visualize the Results:
Once armed with the outcomes of the proximity analysis, it’s time to visualize the results. Merge the beautifully styled river map with the proximity analysis findings. Employ symbols or markers to highlight the precise locations of identified dams. Adjust transparency and layering to ensure that both the categorical river data and dam locations are distinctly visible on the map.
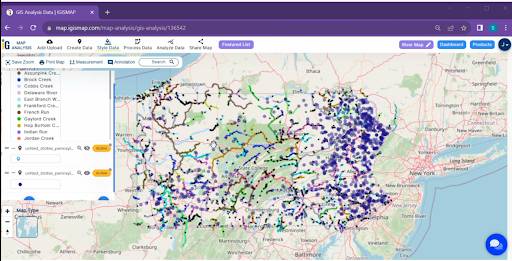
Now comes the moment of interpretation. Study the map closely, examining the distribution of dams along differently colored river segments.
Major Findings:
The analysis revealed several noteworthy findings specific to :
- Clustered Dam Locations: Certain regions exhibited a higher concentration of dams, indicating potential areas of interest for further study.
- Spatial Correlations: Patterns in dam distribution correlated with topographical features in , emphasizing the impact of geography on infrastructure development.
Beneficial Domains:
The insights gained from this geospatial analysis in hold significant implications for various domains:
- Hydroelectric Power Generation: Understanding the proximity of dams to river networks is critical for optimizing hydroelectric power generation .
- Agriculture: Identifying dams along rivers aids in water resource management for agricultural purposes .
- Urban Planning: Insights into the spatial relationships between rivers and dams contribute to inform urban planning, especially in ‘s areas prone to flooding.
In conclusion, the combination of category styling and proximity analysis in MAPOG offers a powerful toolkit for unravelling the spatial relationships between river networks and dams . The findings have broad applications in domains ranging from energy generation to sustainable development within the state. This geospatial approach not only enhances our understanding of landscape but also provides valuable insights for making informed decisions in various fields.
Link of the Data:
Explore the data further through our GIS Data product, uncovering valuable information for in-depth analysis and understanding.