In emergency management, the strategic placement of fire stations plays a critical role in ensuring the safety and well-being of communities. Rapid response times can mean the difference between containment and devastation during a fire emergency. MAPOG offers powerful tools for evaluating potential fire station locations by analysing accessibility to road and travel time to crisis prone areas. This article explores the application of MAPOG in fire station site evaluation, emphasising the importance of data-driven decision-making for effective emergency response planning.
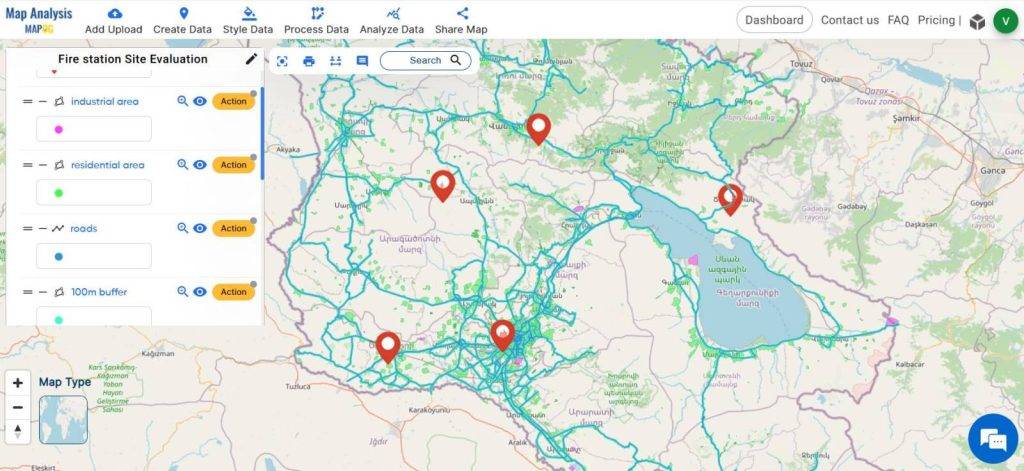
Key Concept of creating map for Fire station site evaluation
The MAPOG buffer tool serves to assess the proximity of fire stations to roads by creating buffer zones around them. This helps in understanding how easily accessible the fire stations are, which is crucial for effective emergency response. The isochrone tool helps to identify the regions that can be reached from the fire stations within a specified time duration. This information highlights the extent of their service area and identifies potential gaps in coverage. The links for GIS Data which we are using here are mentioned at the end of the article.
Follow the below process Step-by-step for Fire station site evaluation
Step 1: Open Map Analysis
Navigate to the Map analysis interface from MAPOG platform.
Step 2: Upload data
To add the required data, click on the Add Upload option from the menu bar at the upper left end.
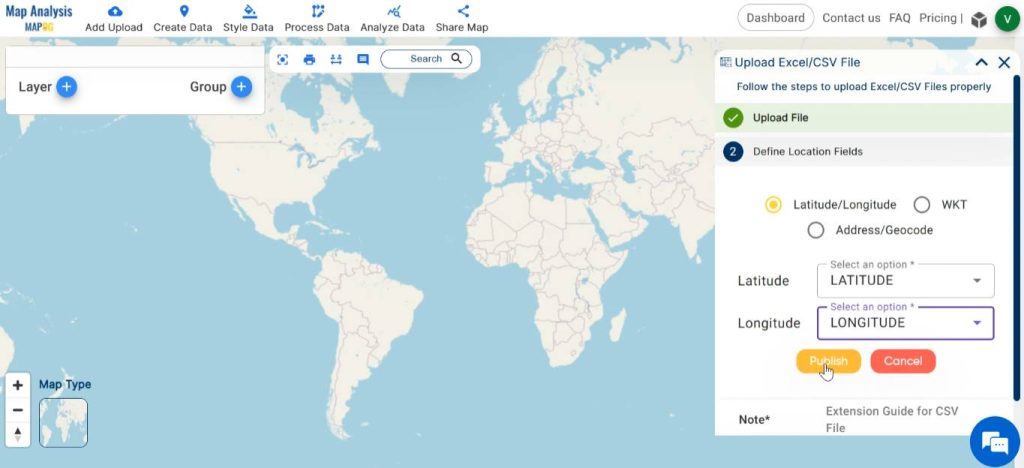
At first add fire station point data as excel file. For this select Upload Excel/CSV file from the Add Upload option.
Browse the file from your device and click on Upload.
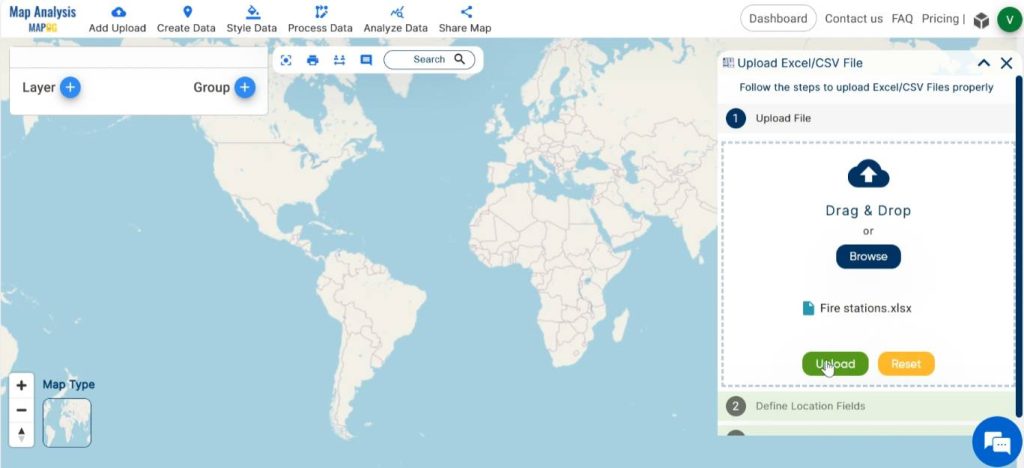
To specify the latitude and longitude columns in the “Define Location Fields” section, choose the respective titles of the columns containing latitude and longitude data from your uploaded file. Finalise by clicking on the Publish button.
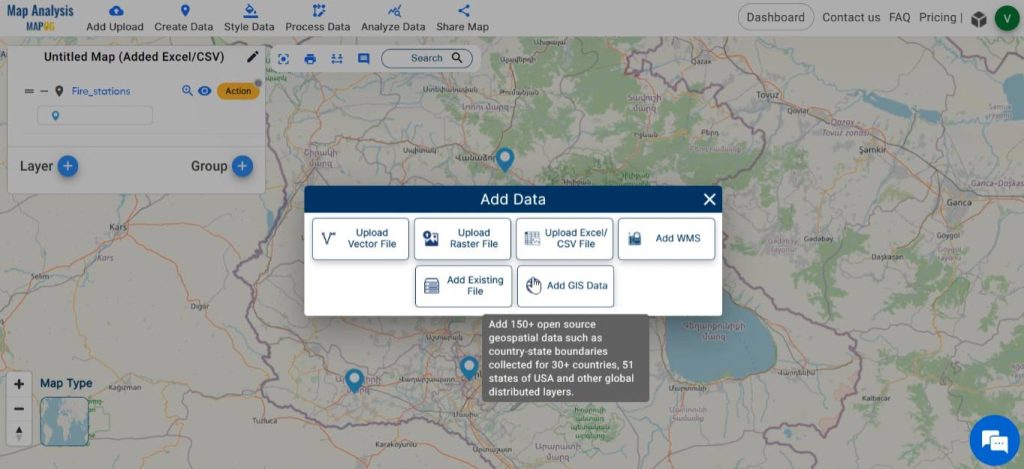
After that, add other data required for analysis. For this click on the Add Upload and then select Add GIS Data.
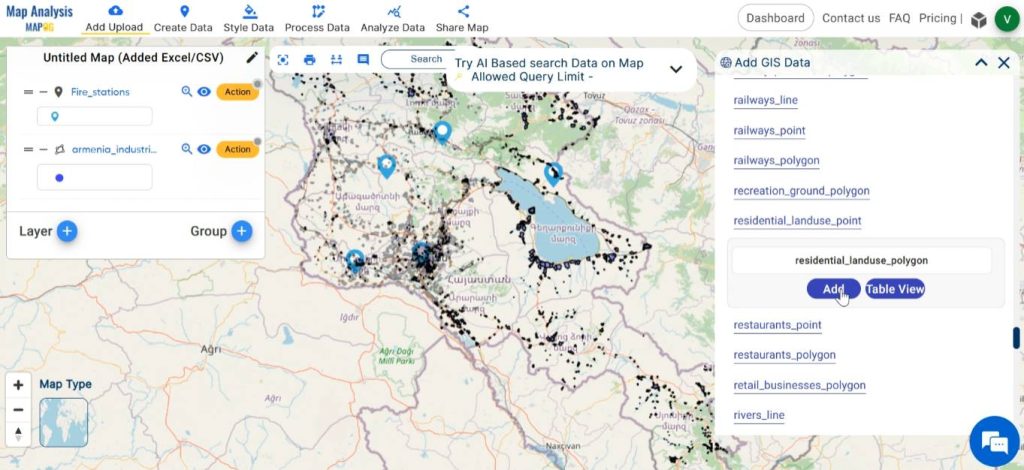
Choose preferred country from the GIS data options. Then, scroll down and select the layers for industrial land use polygon, residential land use polygon, road and add them. After selecting the layer, the Table view option facilitates the preview of the data table.
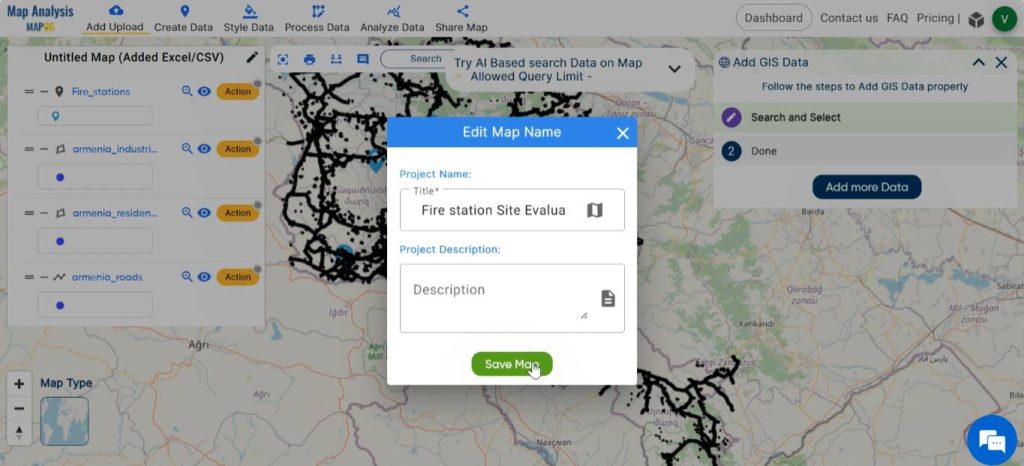
Step 3: Save map
Appropriately name and save your map. Click on the pencil icon next to “Untitled Map” to edit the map title. Enter a suitable name, and if needed, provide a brief description of your project. Finally, save the map by clicking on the Save Map button.
Step 4: Enhance the layers
To rename the layers, click on Action next to the layer and choose the pencil icon. Enter an appropriate name, then click Save.
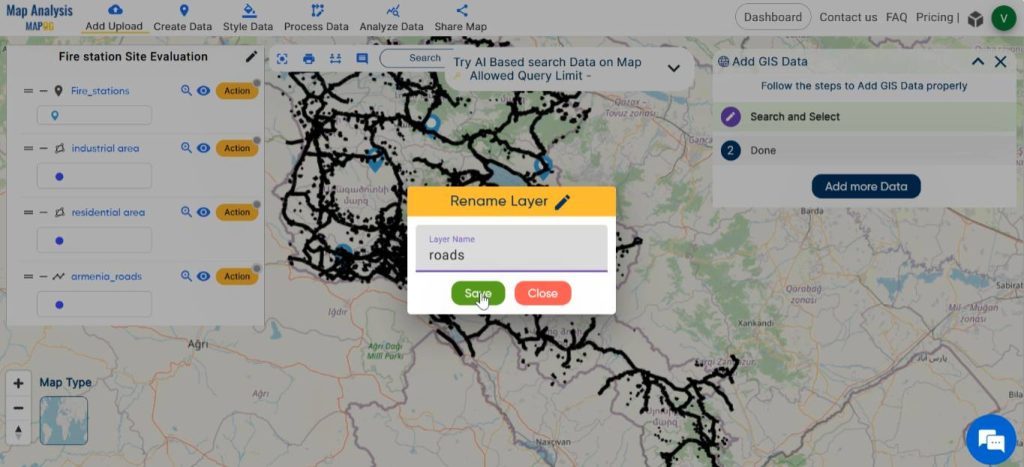
Continue by styling the layers using suitable colours. Select Basic Style from the Style Data in the menu bar. Basic style can be also enabled by clicking on Action, then Edit style and selecting Basic style.
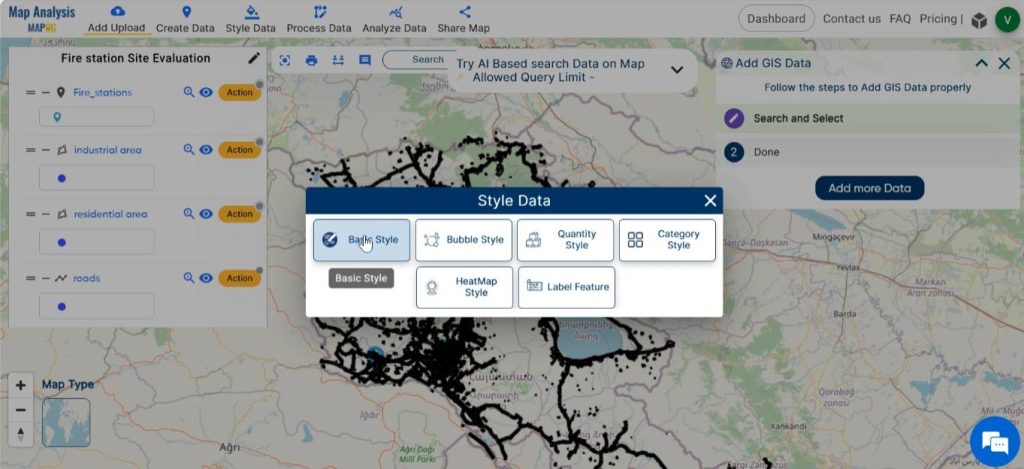
Choose an appropriate icon for the point layer. Style other layers with suitable colour gradients. Save the changes by clicking on save style.
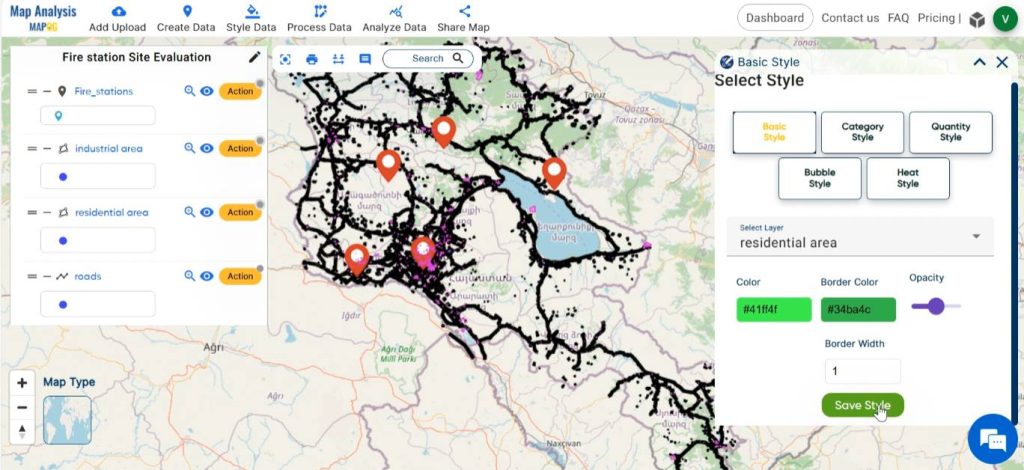
Step 5: Create Buffer
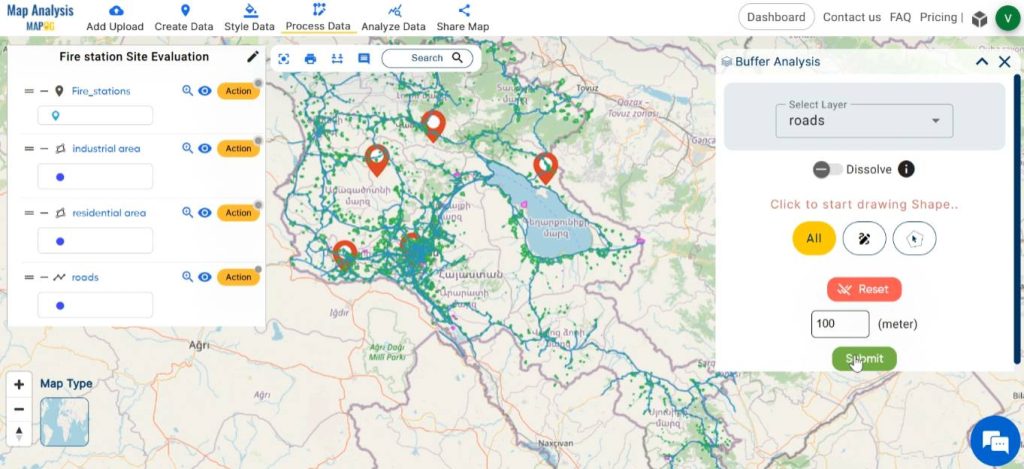
In order to evaluate whether the fire stations are at an easily accessible distance from roads, create buffer zones around roads. To do this, click on Process Data and select Buffer Tool.
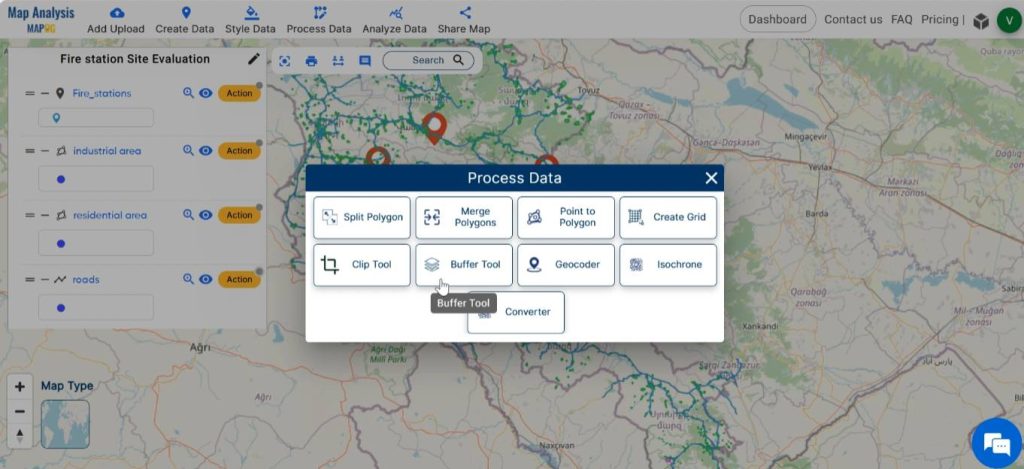
Choose the road layer as the layer to be buffered. Enter the appropriate range, like 100 metres. Then click on Submit.
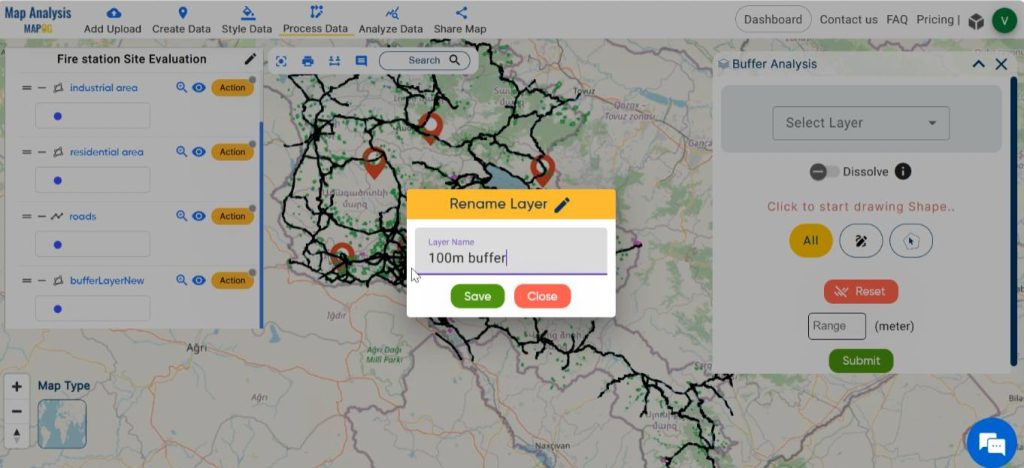
Step 6: Customise the Buffer Layer
Rename the layer by clicking on Action and then selecting the pencil icon. Enter a suitable name and then click on save.
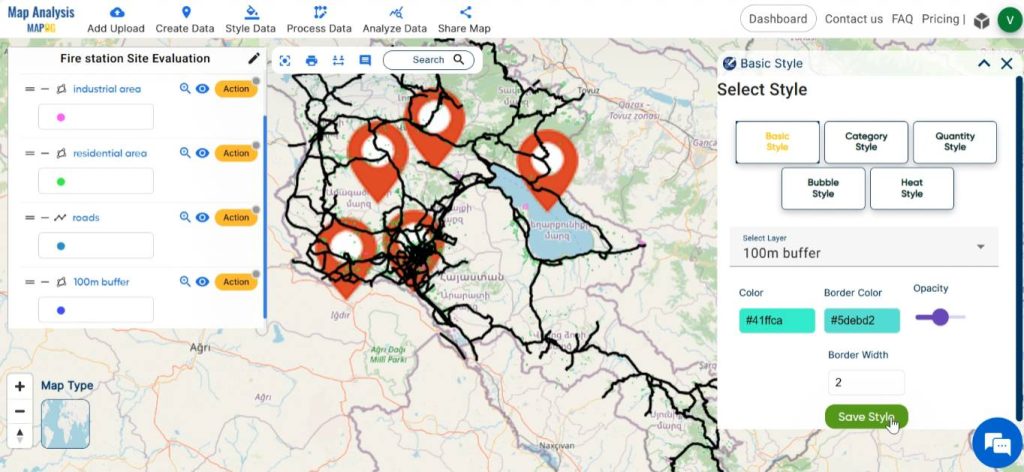
Select basic style from Action or Process data. Choose a suitable colour gradient and save the style.
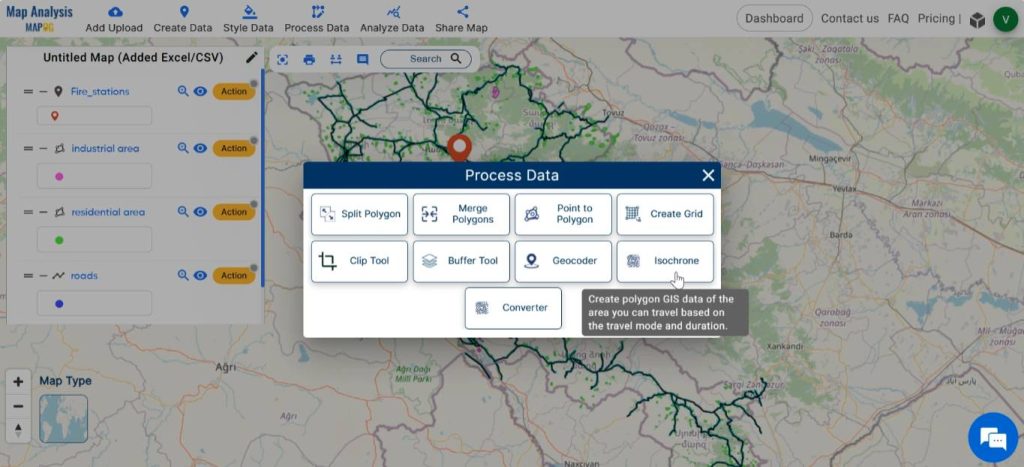
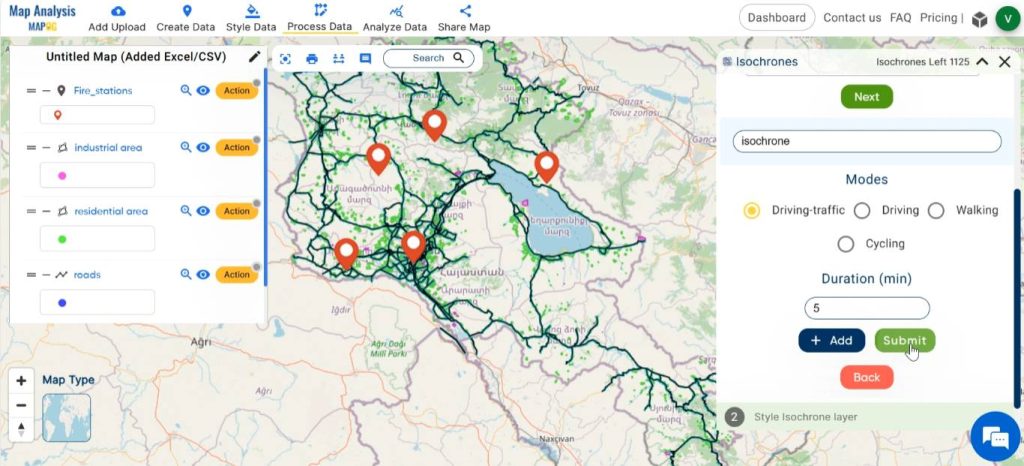
Step 7: Create isochrone
To identify the regions which can be reached from fire stations immediately, create isochrone. Click on Process Data, select Isochrone.
Select the fire station layer. Provide an appropriate name for the new isochrone layer. Enter the desired time duration in minutes. Then, click on submit.
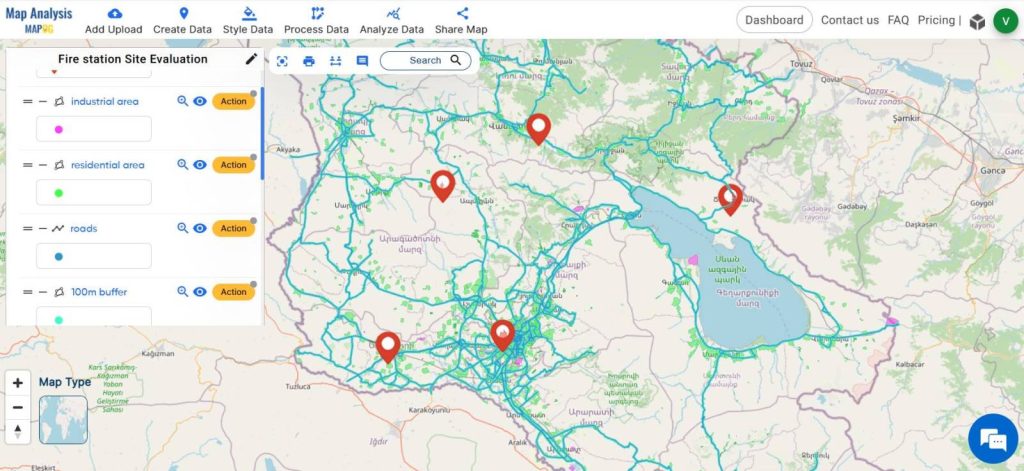
Finally, we have generated a map depicting the accessibility of fire stations to nearby roads and the areas reachable from the fire stations immediately. This data evaluation assesses if the stations are situated in suitable locations.
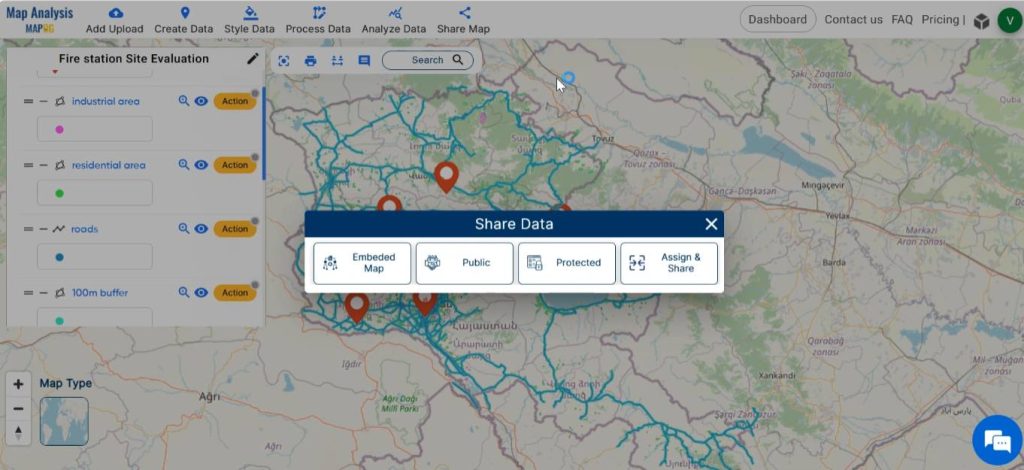
Step 8: Share Map
At last , using the Share tool, share the map or post it on social media.
MAJOR FINDINGS–Fire station site evaluation
- Coverage area: The map delineates the geographic extent within which emergency response services can reach within the specified time frame, thus providing a spatial representation of service availability to different parts of the community.
- Identification of Coverage gaps: Gaps in coverage areas can be identified on the map, highlighting areas that may experience longer response times. This can inform decisions regarding the placement of additional fire stations or the optimization of existing resources.
- Stakeholder Engagement: The map serves as a visual aid for engaging stakeholders in the decision-making process. Allowing the identification of optimal fire station locations that best serve the needs of the community.
DOMAIN AND INDUSTRY
- Emergency Responders: Well-placed fire stations enable them to reach incident locations quickly and effectively enhancing their ability to carry out rescue operations.
- Government: They benefit by optimising the allocation of resources and improving overall emergency management capabilities.
- Urban Planners: This analysis helps in land use planning decisions, infrastructure development, and community resilience strategies.
- Community Organisations: The valuable data from this analysis support their initiatives and efforts during disaster preparedness and response.
- Insurance companies: Insurance companies may benefit from reduced claims and losses resulting from improved fire protection services in areas where fire stations are strategically located.
- Businesspersons: Businesses located within the coverage area of optimised fire stations benefit from enhanced fire protection services.
CONCLUSION-Fire station site evaluation
MAPOG plays a pivotal role in fire station site evaluation by assessing accessibility to road networks and also by analysing coverage areas within specific time intervals. By leveraging this technology, planners can make informed decisions to strategically place fire stations, enhance emergency response capabilities, and ensure the safety and well-being of communities.
GIS Data Links
Other Articles
- Protecting Wetlands: Guide to Create GIS Map for Nature
- GIS Analysis in Urban Planning: Reshaping Transportation Future Insights of state/city
- Fast Emergency Response: Using GIS and Isochrone Maps for 10-Minute Ambulance Arrival
- Mapping Tiger Attack Hotspots – Create an Online Map and Share
- Make Routes for Military Aerial Planning- Through Bearing angle and Distance calculation – Online Route Compass
- Mapping Healthcare Efficiency: GIS Buffer Analysis of Hospital Locations
- Add WMS- Two step online view of WMS layer on a map
- Plot ATM locations on a map and embed on your website
- Map habitat locations of endangered animals & keep track of their living