GIS (Geographic Information Systems) plays a transformative role in the Road Network Analysis development and analysis of infrastructure, particularly in designing and optimizing road networks. By integrating spatial data with planning tools, GIS enables engineers, urban planners, and policymakers to make data-driven decisions. It supports the entire infrastructure lifecycle—from feasibility studies and planning to construction and maintenance—by offering detailed insights into terrain, traffic flow, population distribution, and land use.
Key Concept: How GIS Supports Infrastructure Development and Road Analysis
GIS supports planning of infrastructure by merging geographical data, demographic information, and transportation models. Based on traffic demands and topographical limitations, it assists in mapping existing infrastructure, identifying gaps, and modeling future route alignments. GIS-based road network analysis involves finding bottlenecks or underserved areas, calculating shortest routes, and assessing accessibility. GIS reduces the negative effects on the environment and society by enabling the strategic placement of new highways, bridges, and urban extensions by superimposing numerous data layers.
Use of GIS in Infrastructure Development and Road Network Analysis
GIS provides a foundation for smart infrastructure development in several key areas:
- Route optimization determines the most economical routes by taking into account traffic, terrain, and road conditions.
- Accessibility analysis gauges how simple it is for local communities to get to public transportation, hospitals, and schools.
- Road networks are aligned with future development zones and zoning restrictions through the integration of urban planning.
- Traffic Congestion Monitoring: This technique uses data to pinpoint places with heavy traffic and provide recommendations for changes.
- An infrastructure gap assessment finds places with insufficient access to roads or transportation.
- Environmental Impact Review: Evaluates the effects of road construction on land usage and natural habitats.
Steps Involved in Using GIS for Road Network Analysis
1. Data Acquisition and Configuration
- Acquire and preprocess datasets relevant to the highway extension project, including traffic volume, vehicle classification, fuel consumption, and anticipated construction-related emissions.
- Integrate air quality monitoring station coordinates, pollutant concentration data, environmental reports, and survey findings into the GIS workspace.
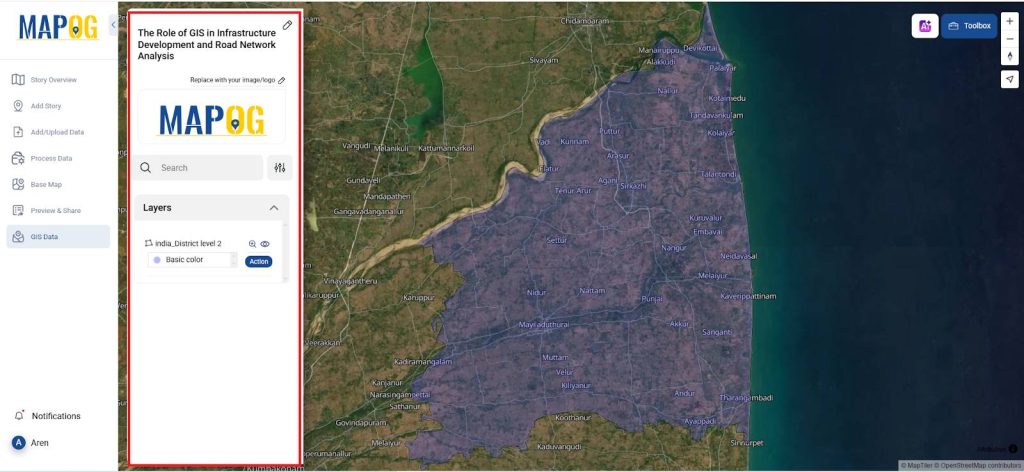
2. District Boundary Layer Integration
- Import administrative boundary layers by navigating through the GIS database: Select Country → State Boundary → District Boundary.
- Load the district boundary as District Boundary 2 and adjust its layer style properties, such as opacity, to enhance underlying map readability and layer distinction.
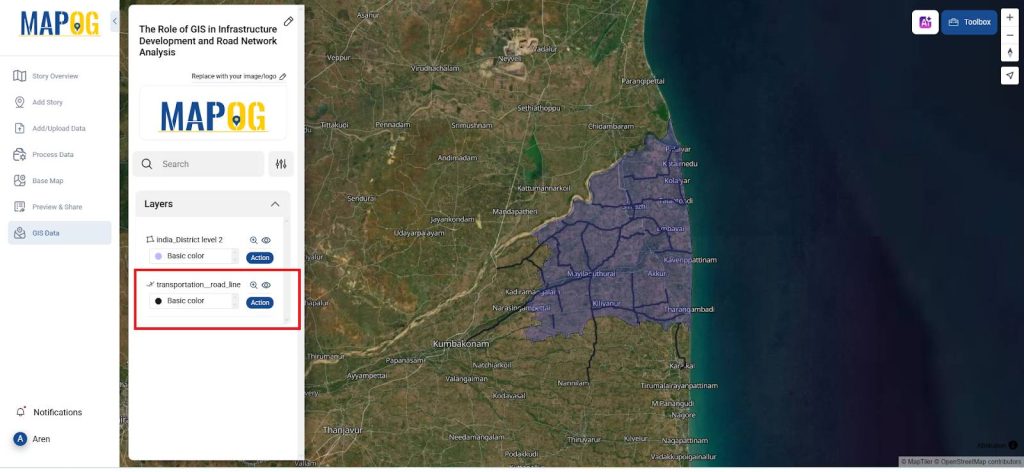
3. Transportation Network Data Import
- Import highway network data via the GIS path: Select Country → State Boundary → District → Transportation: Road line.
- To improve map understanding, apply Style layer in Action (e.g., line color and thickness) to visually distinguish the highway layer from nearby infrastructure.
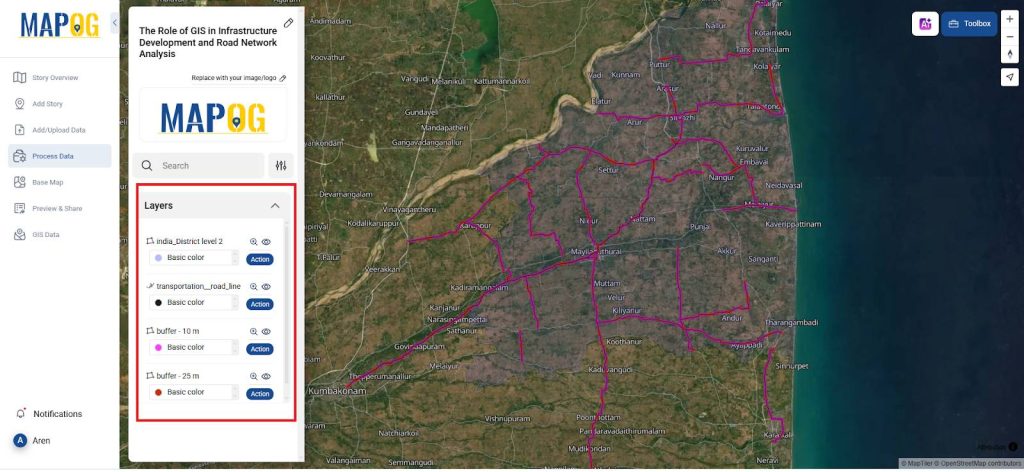
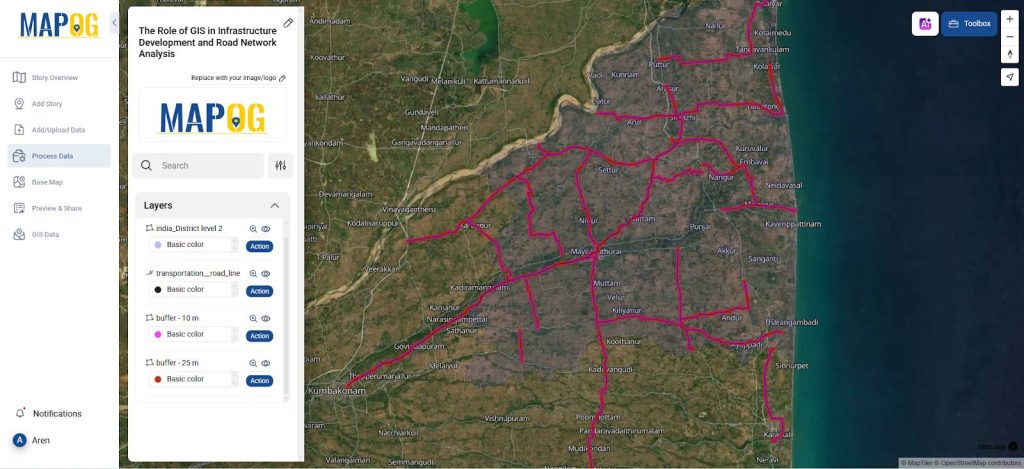
4. Buffer Generation
- Utilize Buffer analysis tools to generate impact zones at specified distances (e.g., 10 m and 25 m) around the existing and proposed highway segments.
- Calibrate buffer distances according to regulatory guidelines, environmental sensitivity zones, or urban development criteria.
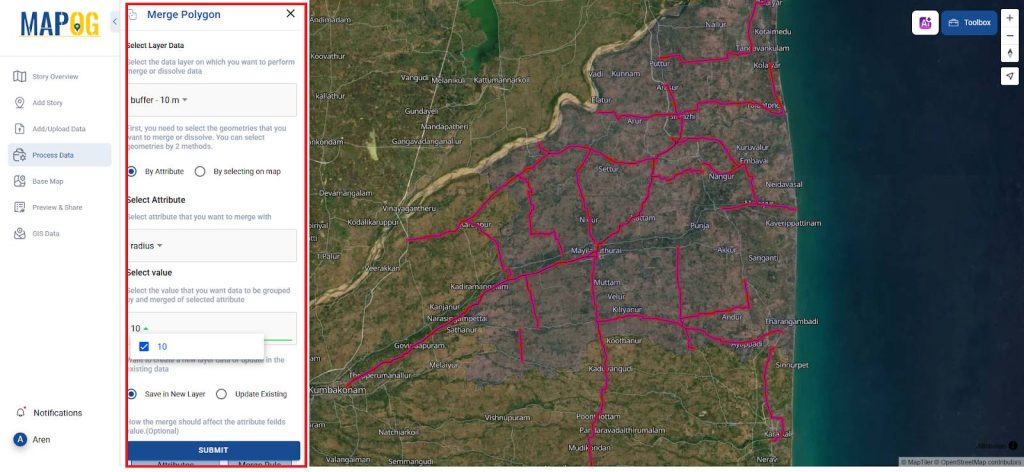
5. Spatially merge Operations
- Conduct spatial join procedures between the buffered zones using Merge polygon in Data Process and in style layer change color for better mapping.
- Extract and associate spatial attributes including ownership details, environmental constraints, and land zoning categories to inform decision-making.
6. Spatial Analysis and Route Optimization
- Perform multi-criteria spatial analysis on the joined dataset to evaluate land suitability, environmental impacts, socio-economic factors, and existing infrastructure interference.
- Determine optimal alignment alternatives for road extension that minimize ecological disruption and acquisition cost.
- Compile a geospatial report summarizing key findings, spatial analytics, and recommended alignment to support planning authorities and stakeholder consultations.
Principal Results in Road Network Optimization
The main outcome is a dynamic GIS platform that streamlines road network planning through multi-layer visualization and advanced spatial analysis. The platform pinpoints underserved regions, high-traffic corridors, and optimal routes, aiding the planning of new infrastructure projects. It enhances the capacity of urban planners and transport authorities to design efficient, inclusive, and future-ready transportation systems.
Industry and Domain
- Industry: Urban Planning, Civil Engineering, Transportation Technology. GIS is leveraged for infrastructure development, from concept design to implementation.
- Domain: Road Network Optimization, Public Transportation Planning, Sustainable Urban Development. GIS enables modeling of transportation systems and integration with smart city initiatives.
GIS Data Used
Conclusion
GIS empowers infrastructure development through precise spatial analysis and data-driven planning. It improves road connectivity, supports sustainable urban growth, and enhances decision-making by visualizing patterns, optimizing routes, and identifying development gaps for smarter, more efficient transportation systems.
An open-source online map-making tool
By utilizing the MAPOG platform, which aids in route planning, spatial analysis, and interactive map production, infrastructure development and road network analysis using GIS is greatly enhanced. This allows for more accurate representation of road networks and infrastructure layouts. By supporting multi-layer overlays and collaborating with urban planners and engineers to streamline development workflows, improve decision-making, and ensure sustainable infrastructure growth. Many of the articles listed below were created with MAPOG.
Explore other Blogs :
- How to Use Convex Hull for Contagious Disease Mapping & Outbreak Control
- Isochrone Analysis in GIS: Optimize Travel Times for Faster Delivery & Urban Planning
- How to Geocode Excel Data and Create an Interactive Map (Step-by-Step Guide)
- Creating Point Data for Urban Planning: Digitizing Settlement Features & Infrastructure Mapping